Bangladesh has made significant progress in disaster risk management, the country is still at risk of growing loss and damage due to disaster and climate stresses. The evidence shows that the current and likely future impact of disaster and climatic stresses on the economy, livelihoods and assets of the country has been pointedly increased in the past decades. Limitations are found in incorporating disaster and climate change risks in all stages of development planning. This extensive linkage between disaster and development generates an urgency to establish a risk information platform/interface to access disaster and climate risk information and tools for risk-informed planning and investment.
At present the available databases for managing development project life cycles, and climate risk screening tools are quite fragmented and lacks contextual data and information on disaster and climate change risks. Databases related to development planning and management located within the Government of Bangladesh do not supply necessary data and information for DPP preparation addressing disaster and climate change risks, rather mainly focusing on DPP submission to implementation, budget management and monitoring. In Contrast, most of the risk screening tools are about physical hazards and risks, and do not follow any integrated approach for risk and vulnerability assessment.
For Bangladesh, to assist in the budgeting process of development projects, a climate risk screening tool has been developed under the project titled “Establishing a Climate Risk Screening System for Mainstreaming Climate Change Adaptation into National Development Budgeting Activities”, funded by Asian Development Bank (ADB) which can help Planning Commission officials to ascertain the impact of climate change in a development project, its economic losses and adaptation need.
This platform/interface is designed to provide necessary disaster and climate risk data and information to carry out Disaster Impact Assessment (DIA), a tool proposed by the National Disaster Management Council of Bangladesh headed by the Prime Minister, to ensure disaster resilient development. However, as such, there is no comprehensive database comprising tools and knowledge product to assist the planners to integrate disaster and climate risk data and information into development projects, plans and programmes for decision making and planning for risk-informed public investment.
This platform provides data and information for disaster and climate risk and vulnerability assessment, and potential climate change adaptation options as well as disaster risk mitigation measures to address identified risks and vulnerabilities caused by the project and also in project implementing areas.
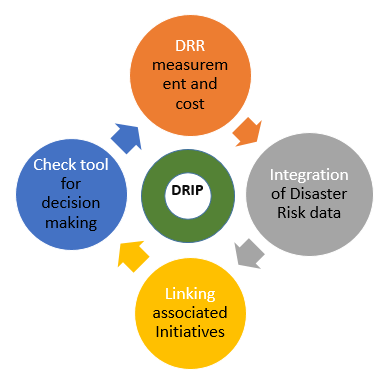
The Disaster and Climate Risk Information Platform (DRIP), a specialized software application, aims to strengthen the institutional capacity of the Government of Bangladesh for assessing, understanding and communicating disaster and climate related risks, with the goal of integrating disaster risk information into development planning & budgeting, policies and programs. The specific objectives of the project are listed below:
Please wait ... . .